nasopharyngeal carcinoma histology
Definition general. Among all cancers the incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC is quite high in the endemic regions.
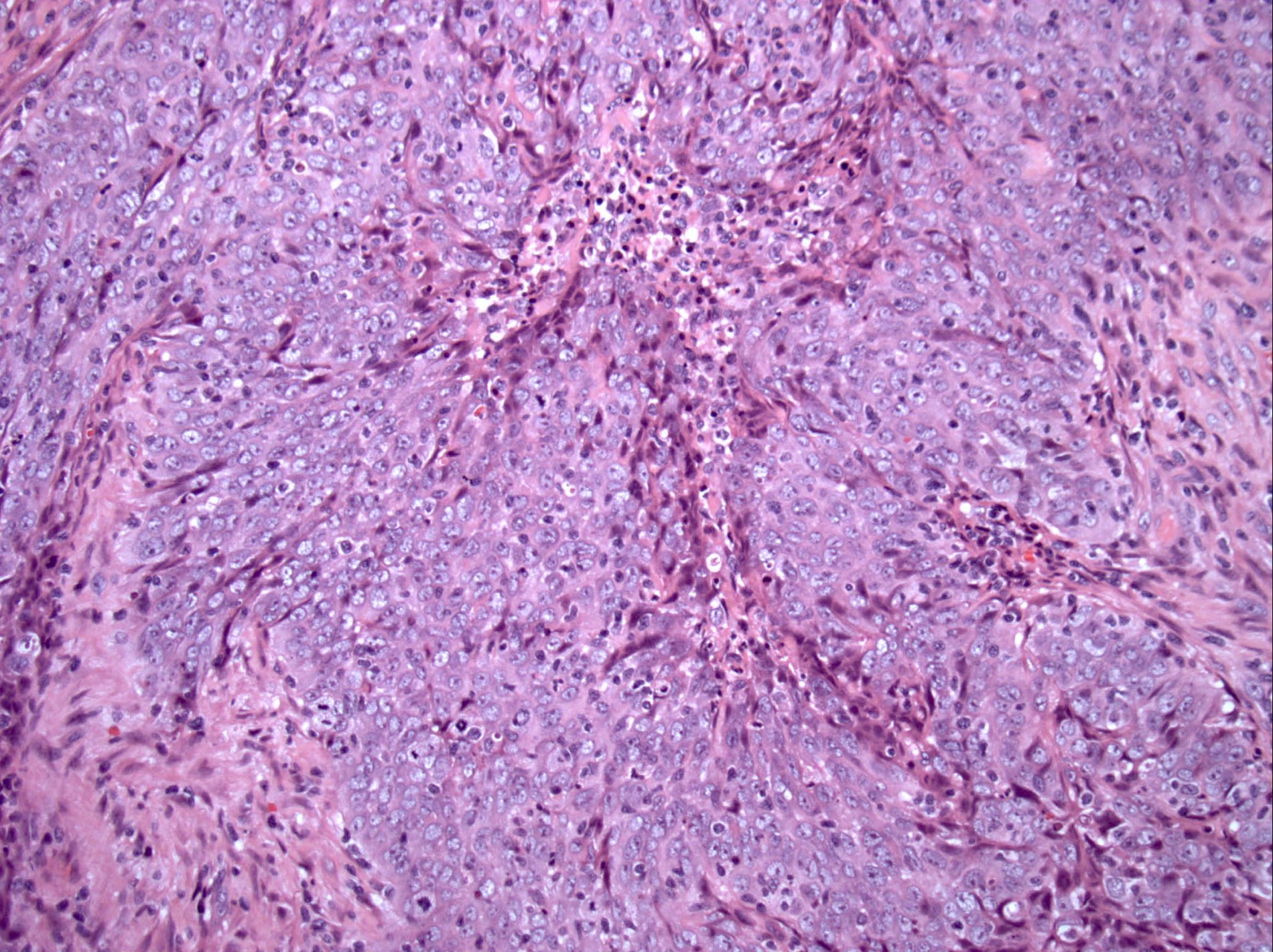
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
The histologic appearances of this carcinoma are varied ranging from squamous cell carcinoma to undifferentiated carcinoma sometimes with different patterns present within the same tumor.

. A clear understanding of. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC or nasopharynx cancer is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess fossa of Rosenmüller accounting for 50 of casesNPC occurs in children and adults. NPC is a head and neck cancer with poor survival rate and is rare throughout most of the world but common in certain geographic areas like southern Asia and some regions of North East India Nagaland Manipur and Mizoram.
The use of the terminology and definitions proposed by WHO would facilitate and improve inte. Diagnosing the disease in the early stages requires a high index of clinical acumen and although most cross-sectional imaging investigations show the tumour with precision confirmation is dependent on histology. The initial histologies of 137 patients were available.
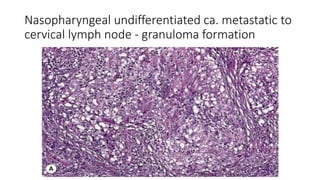
Necrotising granulomata present in metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma have been described in the literature 1 but there is paucity of published material concerning this phenomenon and how it can affect clinical decision making. Prognosis and histology in Stage I nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC. Nasopharyngeal carcinomas account for a 70 majority of malignancies arising in the nasopharynx.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a type of cancer that starts from an area at the back of the nose and throat called the nasopharynx. Nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Pediatric nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC is a rare epithelial origin tumor associated with undifferentiated histology Epstein-Barr virus EBV infection and genetic risk factors.
WHO classification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Histological typing of nasopharyngeal carcinoma There is little agreement about correlations between histological type and the epidemiological and biological characteristics of NPC. It is commonly diagnosed between 40 and 60 years.
The etiology is multifactorial with race genetics environment and Epstein-Barr virus EBV all playing a role. Histomorphological features of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC is a head and neck tumour that can present with cervical lymphadenopathy.
Epstein-Barr virus EBV-encoded RNA signal is present in all nasopharyngeal. The World Health Organization classifies nasopharyngeal carcinoma into three types. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma nasopharyngeal papillary adenocarcinoma Sinonasal carcinoma.
Sinonasal carcinoma-general HPV related multiphenotypic carcinoma NUT carcinoma sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma neuroendocrine carcinoma including small cell carcinoma SMARCB1 deficient sinonasal carcinoma squamous cell. Incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma has remained high in endemic regions. Saw D Ho JH Fong M Chan CL Tse CH Lau WH.
Most cases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma are caused by a virus known as Epstein-Barr virus EBV which infects the cells on the inside of the nasopharynx and causes them to change into cancer cells. Although this tumor is of squamous cell in origin the etiology and its pathogenesis epidemiology ie geographical distribution and ethnicity and biological behavior are. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma accounts for 70 of all primary malignancies of the nasopharynx and although rare in western populations it is one of the most common malignancies encountered in Asia especially China 13-5.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma originates from the nasopharyngeal mucosa showing histologic or immunophenotypic evidence of squamous differentiation. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC constitutes the most common epithelial malignancy of the nasopharynx and shows a strong geographic variation. To establish a new histologic classification with better correlation with patient prognosis the histologic features of nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC were correlated with prognosis and clinical stage among 494 patients who had been followed a minimum of 5 years after initial radiotherapy.
It differs from other head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in epidemiology histology natural history and response to treatment. The most common type of nasopharyngeal tumor is nasopharyngeal carcinoma. An Introduction Nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC of undifferentiated type is a tumor whose unique pathogenesis involving genetic lifestyle and viral cofactors has made it an important platform for research on.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is the predominant tumor type arising in the nasopharynx the tubular passage behind the nasal cavity that connects to the oropharynx below. The diagnostic term nasopharyngeal carcinoma is used to describe SCC that occurs primarily at nasopharyngeal mucosa. NPC differs significantly from other cancers of the head and neck in its occurrence causes.
Males are more commonly affected with a male to female ratio of 31. During 1969-1975 212 new patients with Stage I nasopharyngeal carcinoma NPC with a tumor apparently confined to the nasopharynx were treated at Queen Elizabeth Hospital Kowloon Hong Kong. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a rare presentation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma that differs from typical squamous cell cancers of the head and neck in etiology histology and treatment response.
Type I moderately differentiated SCC. Childhood NPC is usually clinically silent often presenting with advanced locoregional compromise including skull base invasion and cervical lymphadenopathy and. While rare in Caucasian populations it is one of the most frequent nasopharyngeal cancers in Chinese and has endemic clusters in Alaskan Eskimos Indians and Aleuts.
The study revealed nonkeratinizing carcinoma as the most prevalent histology at 943 undifferentiated type 859 and differentiated keratinizing squamous cell. This is largely due to variations in terminology and diagnostic criteria.
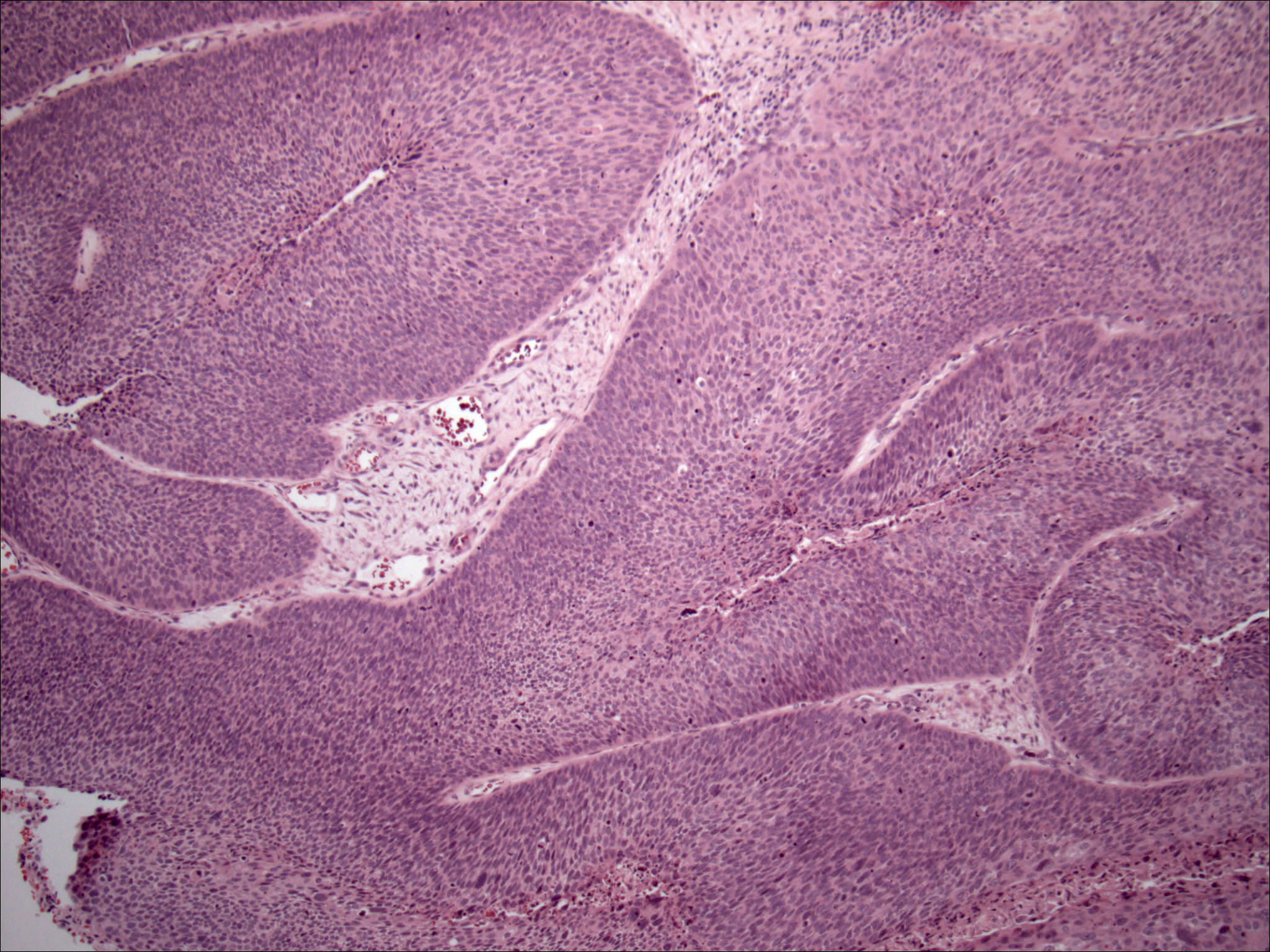
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Histopathology Of The Nasopharyngeal Lesion Photomicrograph Of The Download Scientific Diagram
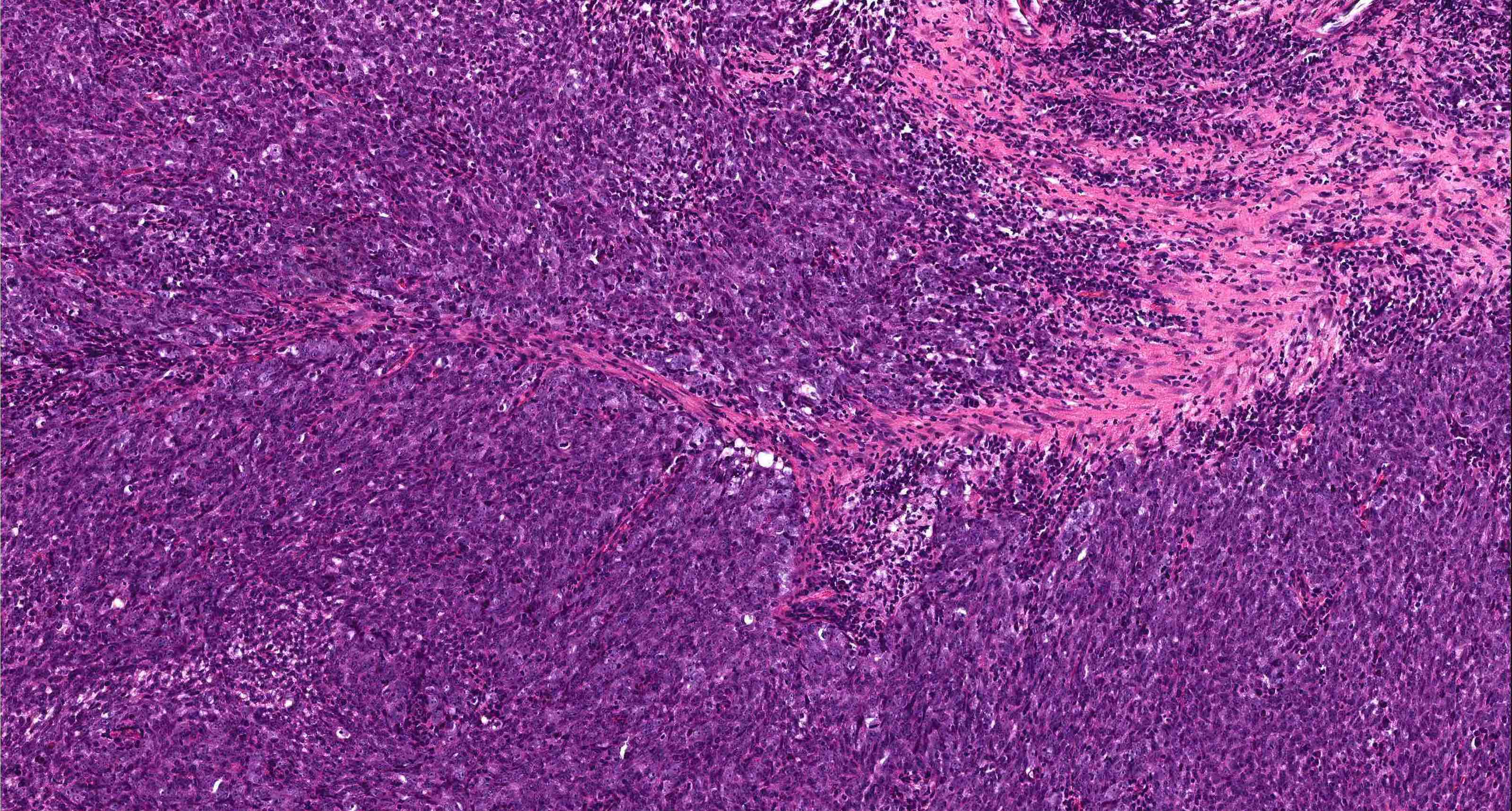
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Amyloid Deposition In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma The Histology Of Download Scientific Diagram
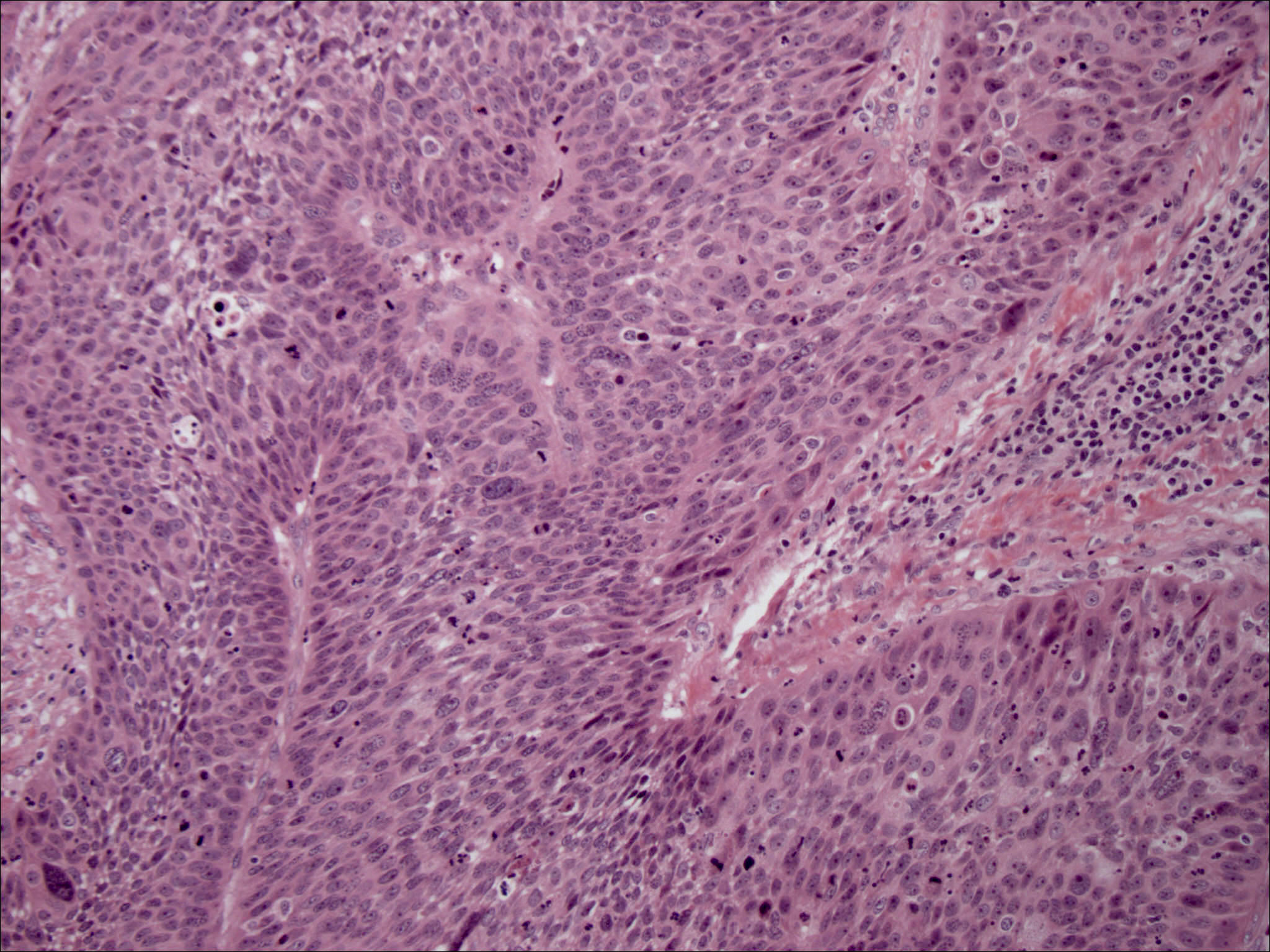
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Histopathology Images Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Undifferentiated By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Undifferentiated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Who G Iii Download Scientific Diagram
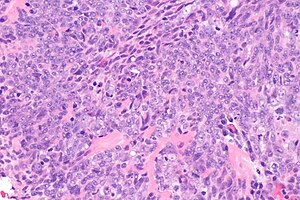
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Libre Pathology
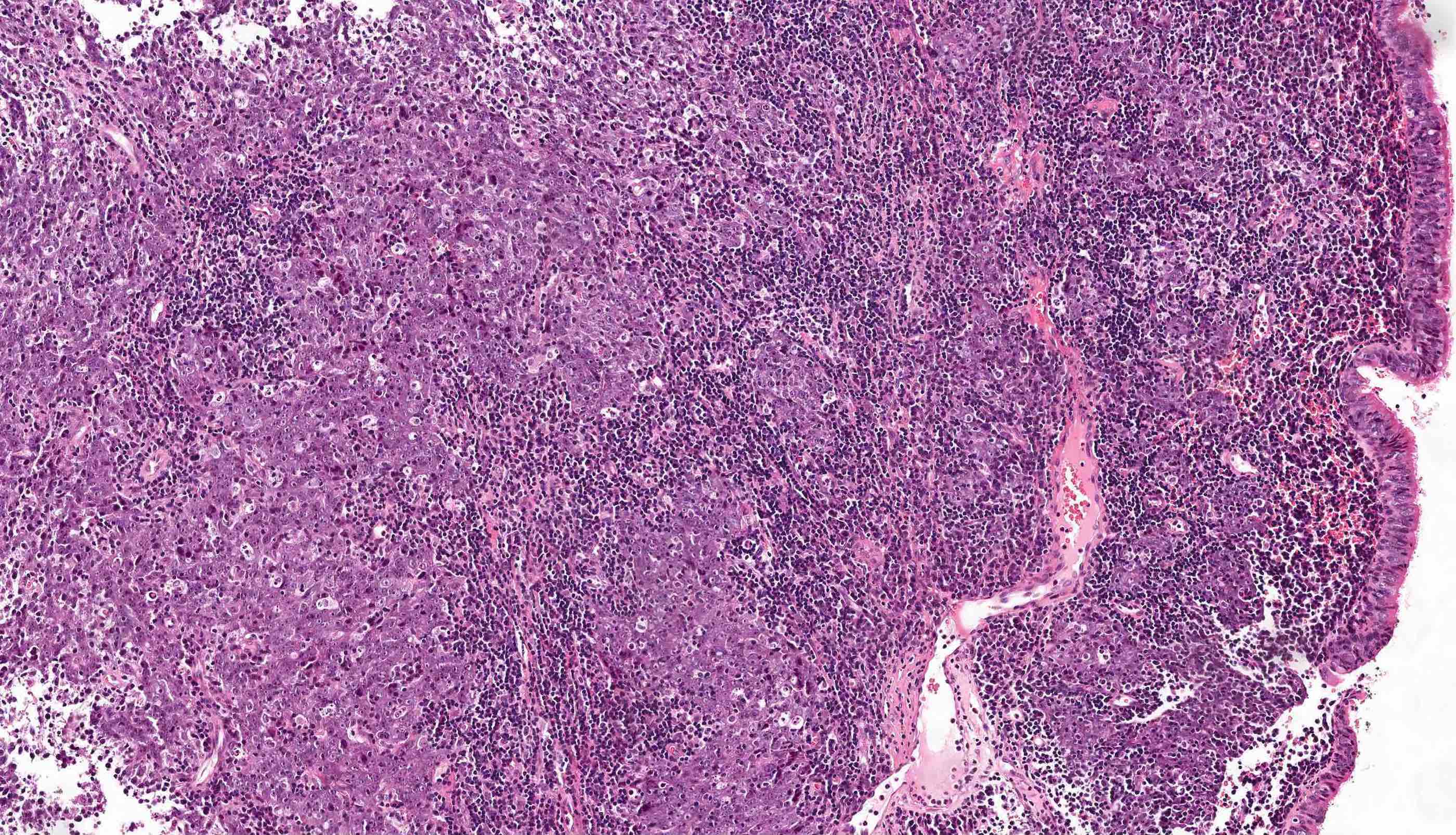
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma

Histopathology Images Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Undifferentiated By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Histopathology Images Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Undifferentiated By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Nonkeratinizing Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma These Tumors Are Further Download Scientific Diagram

Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Mypathologyreport Ca
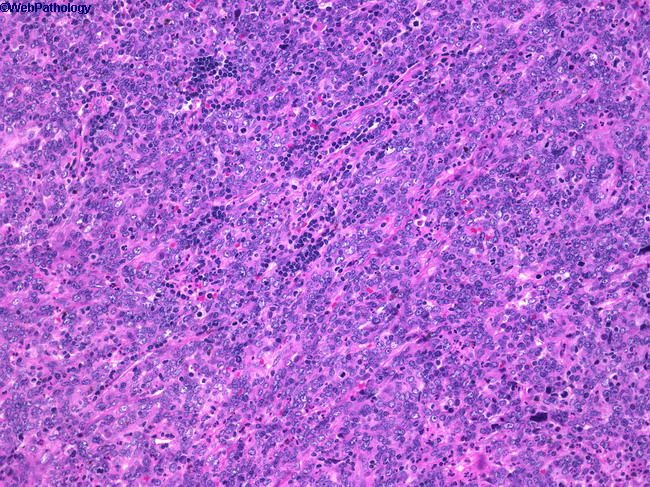
Webpathology Com A Collection Of Surgical Pathology Images
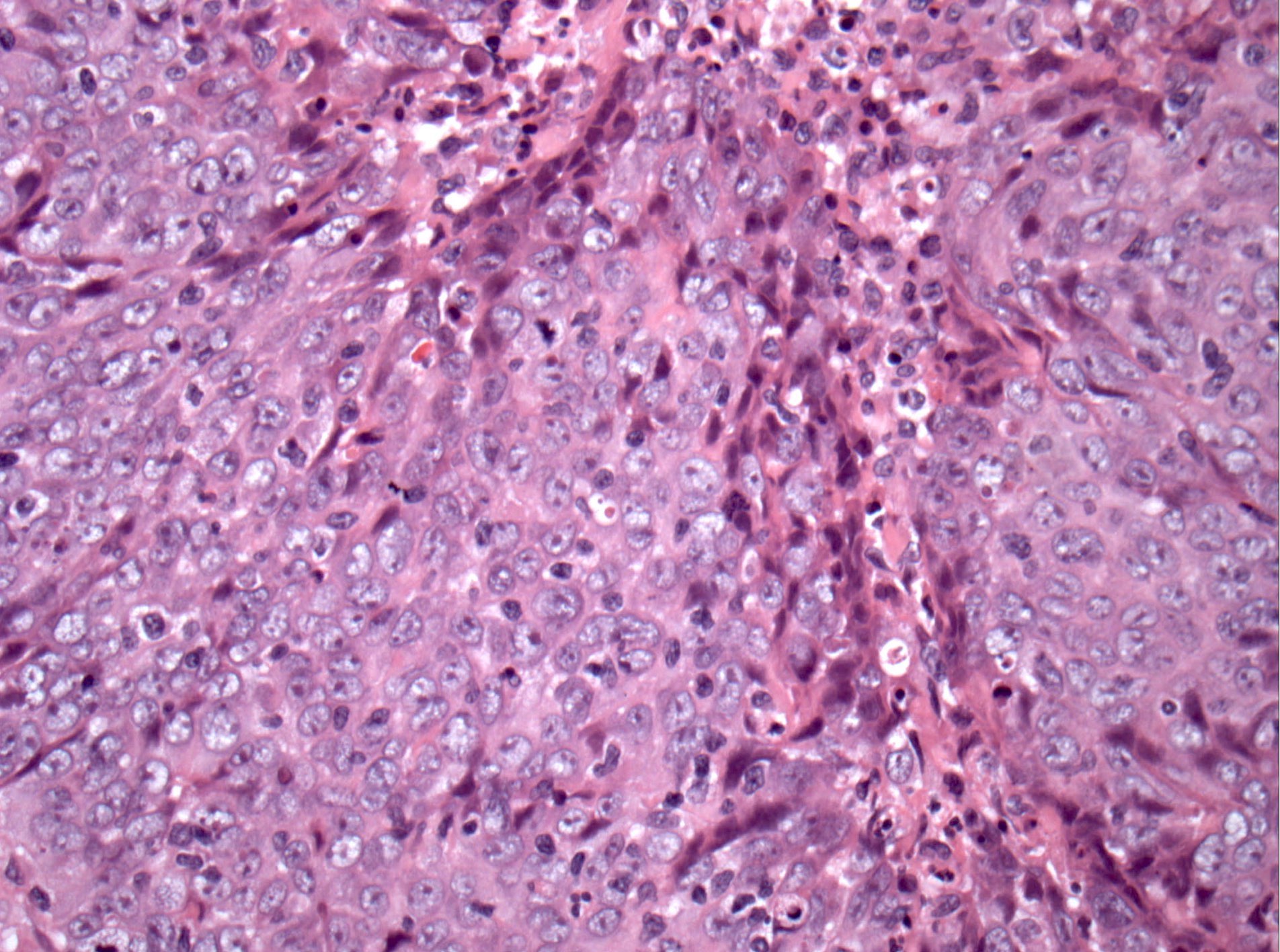
Pathology Outlines Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Histopathology Picture Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Showing Invasive Download Scientific Diagram

Histopathology Images Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Undifferentiated By Pathpedia Com Pathology E Atlas

Pdf Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma An Analysis Of Histological Subtypes And Their Association With Ebv A Study Of 100 Cases Of Pakistani Population Semantic Scholar
0 Response to "nasopharyngeal carcinoma histology"
Post a Comment